New design LED high bay light 70W
New heat dissipation technology for 100W LED high bay light
MOQ :10 piece
Lead Time :7 Days
Seller Support : Trade Authenticity Guaranteed & Accepting
Payment : L/C,T/T,Western Union,Other
Departure Port : Shenzhen
Product details
Supply Ability
- Supply Ability:5000 piecesWarranty(Year):3 Year
Packaging & Delivery
- Length:495 cmWidth:355 cm
- Height:435 cm
- Packaging:1 piece
Product Specifications
Product Description
Input voltage: AC100-240V 50-60HZ
Beam angle: 60°,100°
Lighting color: cool white (5000-6000k), pure white (4000-4500K) Warm white(2700-3000K)
CRI >80
Recommend installation 8-10m
Features:
1.Can replace with different light under normal environment, also can work as anti-explosive light [[[[[[[[and]]]]]]]] anti-corrosion light,
2. Heat dissipation: NEW technology of phase change, make LED TJ is below 65 degree, ensure lamp stability [[[[[[[[and]]]]]]]] long life.
3.American orginal package LED, high brightnes, low light decay.
4.Large current allowance, high quality insurance, Taiwan MW driver, meet the st[[[[[[[[and]]]]]]]]ard of global lighting equipment.
5.Equal to 250W HPS lamp.
6.Long life >30,000hours, easy installation.

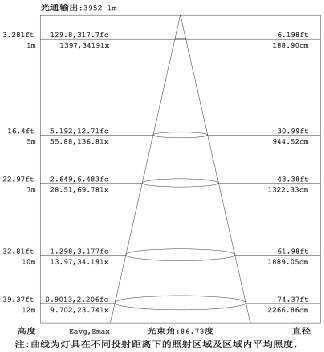
Light distribution curve:

Average luminaire drawing:
What is Taidilen LED high bay light heat sink difference with other company`s bay light ?
Typical heat pipe comprises of pipe shell, liquid absorption core [[[[[[[[and]]]]]]]] end cap. After pumping down the air pressure within the pipe to the negative pressure of 1.3 x (10negative1—10negative4) Pa, it imbues appropriate working liquid. This makes the liquid absorption porous capillary clinging to the pipe wall hermetic by fulfilling liquid. One end of the pipe is evaporation segment (heating segment), the other end of pipe is condensation segment (cooling segment), [[[[[[[[and]]]]]]]] adiabatic segment could be disposed between two segments according to the application necessary. When one end of heat pipe is heated the liquid in the capillary core evaporates, steam flows to the other end under slim pressure difference [[[[[[[[and]]]]]]]] liquefies by release quantity of heat, then liquid flows back to the evaporation segment along the porous material depending on the capillary force. By such [[[[[[[[and]]]]]]]] such cycle, the quantity of heat is transferred from one end to the other end. In the process of implementing this heat transfer the heat pipe includes the following six correlative main processes:
(1) Heat is transferred from the heat source to the liquid-gas interface depending on the heat pipe wall [[[[[[[[and]]]]]]]] working-liquid-fulfilled liquid absorption core;
(2) Liquid evaporates on the liquid-gas interface within the evaporation segment;
(3) Steam in the steam cavity flows from the evaporation segment to the condensation segment;
(4) Steam condensates on the liquid-gas interface in the condensation segment;
(5) Heat is transferred from the liquid-gas interface to the cold source depending on the liquid absorption core, liquid [[[[[[[[and]]]]]]]] pipe wall;
(6) In the liquid absorption core the liquid condensate refluxes to the evaporation segment as a result of capillary function.


You May Like
- Free Member
- Trade Assurance
Business Type : Manufacturer,Exporter
Company Location:
Year Established: 16YRS
You May Like
-

New design LED high bay light 70W
-

60W Solar LED street light
-

120W LED street light
-

180W / 200W LED high bay light
-

SAA 200W LED high bay light 2014 new price
-

36W linear led tube lighting 4ft
-

Cree / Bridgelux high bay light 100W 120W 150W
-

16W / 18W 1200mm LED Tube
-

Single COB 40W LED street light
-

Europe style 20W 36W 45W 54W LED linear light,easy to install and maintenance







